Meta Description: Explore the importance of arc resistance in material selection to ensure safety, reliability, and durability in electrical systems.
The Significance of Arc Resistance in Material Selection

Electrical faults and equipment failures can halt operations, cause costly downtime, and pose a threat to worker safety. In fact, around 80% of electrical injuries involve thermal burns from arc flash events.
These incidents represent real financial losses, operational delays, and safety hazards for engineers and manufacturers. Selecting the right materials for electrical systems can drastically reduce the likelihood of such catastrophic events, safeguarding both personnel and equipment.
In this blog, we will discuss why arc resistance matters in material selection and its critical role in preventing failures, enhancing safety, and maintaining system reliability.
What Is Arc Resistance?
| Arc resistance refers to a material’s ability to withstand the effects of electrical arcing without sustaining damage or losing its structural integrity. |
Electrical arcs generate intense heat and light, which can rapidly degrade materials that cannot endure such stress. Materials with high arc resistance are essential in electrical systems, as they help prevent equipment failure, reduce maintenance costs, and protect personnel from electrical hazards.
Materials with proper arc resistance are commonly used in switchgear, circuit breakers, and other electrical components where high-voltage faults or short circuits may occur. Selecting materials that can resist arcing ensures both reliability and safety across electrical installations.
Major aspects of arc-resistant materials include:
- Ability to endure high temperatures without melting or deforming
- Resistance to surface erosion or carbonization caused by arcing
- Maintenance of insulating properties during and after an arc event
- Prevention of fire propagation in case of electrical faults
By considering these factors, engineers can significantly reduce the risks associated with electrical arcs and improve the longevity and performance of electrical systems.
Importance of Arc Resistance
Below are the major reasons why arc resistance is important.
Preventing Safety Hazards
Electrical arcs generate extreme heat and energy. Without proper resistance, materials can melt, ignite, or degrade, leading to equipment damage, fire risks, and severe threats to personnel safety.
Improving Equipment Reliability
Arc-resistant materials preserve performance under stress. Unlike low-resistance alternatives that wear down quickly, they maintain integrity, reduce failures, and extend the lifespan of electrical systems.
Reducing Costs and Downtime
Frequent replacements or repairs from arc damage can become costly. By investing in arc-resistant materials, organizations cut long-term expenses and avoid costly system downtime.
Ensuring Compliance and Standards
In high-voltage and industrial applications, material selection is crucial. Arc resistance helps meet stringent safety and performance standards, protecting both operations and reputation.
How Is Arc Resistance Tested?
Arc resistance testing evaluates a material’s ability to withstand electrical arcing without significant damage.
Standardized tests, such as ASTM D495, involve applying a controlled arc to the material surface under laboratory conditions and measuring the time until failure or visible degradation occurs. This provides a quantifiable measure of the material’s ability to resist arc-induced damage.
Additional tests focus on more challenging conditions:
- Wet surface tests (ASTM D2132): Assess how moisture affects the material’s arc resistance.
- Contaminated surface tests (ASTM D2303): Examine performance under pollution, dust, or chemical residues.
- Standard dry tests (ASTM D495): Measure baseline arc resistance under controlled conditions.
Interpreting test results requires understanding both the material’s performance under standard and extreme conditions. Materials with higher arc resistance ratings can sustain repeated or prolonged arcs, making them suitable for high-voltage or critical safety applications.
Designers and engineers use these insights to select materials that enhance safety, reliability, and longevity in electrical equipment.
Factors Affecting Arc Resistance
Arc resistance is not solely a property of the material; several environmental and operational factors influence it. Understanding these variables helps engineers select the right materials and design equipment to withstand electrical stress safely.
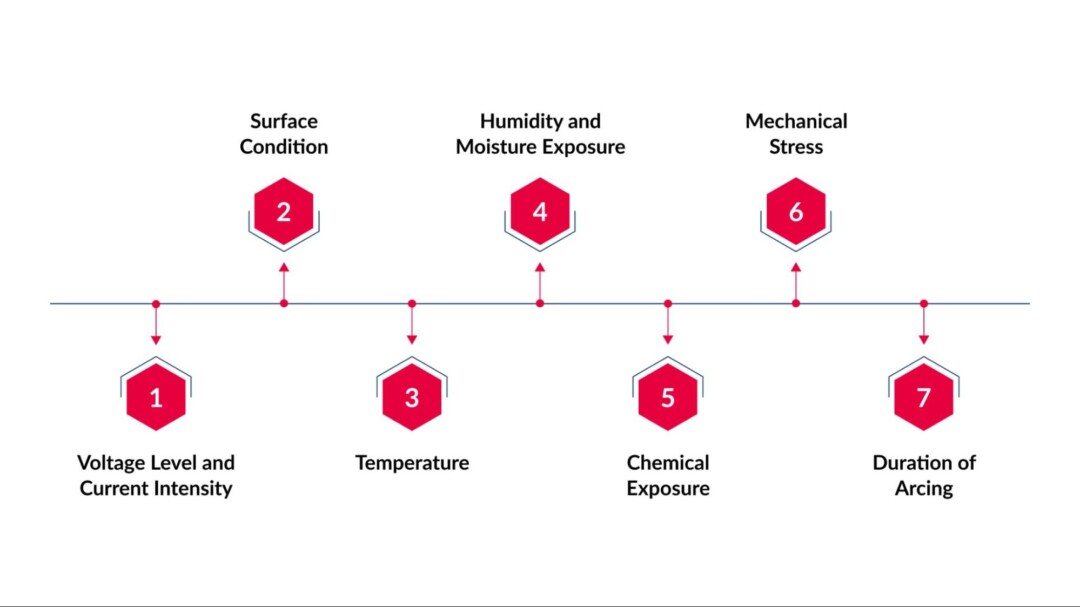
- Voltage Level and Current Intensity: Higher voltages or currents can create more severe arcs, requiring materials with higher resistance to prevent surface breakdown and carbon tracking.
- Surface Condition: Smooth, clean surfaces generally resist arcing better than rough or contaminated surfaces. Dust, oil, or moisture can lower the effective arc resistance significantly.
- Temperature: Elevated operating temperatures can soften or degrade insulating materials, reducing their ability to withstand electrical arcing over time.
- Humidity and Moisture Exposure: Moist environments increase the risk of tracking and surface discharge, lowering arc resistance. Materials must retain insulating properties even under wet conditions.
- Chemical Exposure: Some chemicals or gases can erode insulating surfaces or react with polymers, weakening their resistance to arcing.
- Mechanical Stress: Physical stress, including bending, compression, or vibration, can create micro-cracks, reducing the material’s ability to withstand arcs.
- Duration of Arcing: Prolonged exposure to arcs tests a material’s endurance. Some materials perform well under short arcs but degrade under repeated or sustained arcing events.
Recognizing these factors ensures the proper selection of materials, design adjustments, and protective measures, helping to prevent equipment failure, fire hazards, and costly downtime.
Materials With High Arc Resistance
Selecting materials with high arc resistance is crucial for electrical equipment, switchgear, and insulating components. These materials can withstand repeated electrical arcing without significant degradation, reducing the risk of fire, equipment failure, or safety hazards.
High arc resistance materials are particularly important in high-voltage environments, industrial machinery, and areas where equipment may be exposed to dust, moisture, or other contaminants.
The most commonly used materials with superior arc resistance include thermosetting plastics, engineered polymers, and certain composites. Each material has unique characteristics in terms of dielectric strength, mechanical durability, and environmental stability.
Engineers often choose materials based on the specific voltage, temperature, and operational conditions of the application.
| Material | Typical Arc Resistance (Seconds) | Common Applications | Key Characteristics |
| Epoxy Resin | 180–220 | Switchgear, insulators, bushings | Excellent mechanical strength, high dielectric stability |
| Phenolic Resin | 150–200 | Circuit breakers, panel components | Good heat resistance, durable under electrical stress |
| Polycarbonate | 120–160 | Protective housings, enclosures | Impact-resistant, transparent, good electrical insulation |
| Polyester (PET, PBT) | 100–140 | Connectors, terminal blocks | Chemical resistance, dimensional stability |
| Melamine Formaldehyde | 140–180 | Electrical switches, insulators | High temperature resistance, flame-retardant properties |
Applications Where Arc Resistance Counts
Selecting materials with high arc resistance is crucial in environments where electrical equipment is subjected to repeated or intense stress. Using the right material prevents insulation failure, reduces maintenance costs, and enhances safety for both equipment and personnel.
- Electrical Switchgear and Panels: Materials with high arc resistance ensure that switches, breakers, and busbars withstand accidental arcs, protecting operators and maintaining system reliability.
- Transformers: Insulating components in transformers must resist arcing during switching operations or fault conditions to prevent short circuits and thermal damage.
- Circuit Breakers and Fuses: Arc-resistant materials prevent tracking or degradation during fault interruption, extending the life of protective devices.
- High-Voltage Equipment: Substations, transmission lines, and industrial machinery often face high voltage stress. Arc-resistant insulators prevent flashovers and maintain safe operation.
- Industrial Automation Systems: Control panels, robotic arms, and machinery in automated facilities require durable insulation to withstand electrical stress without compromising performance.
- Railway and Transportation Systems: Switches, contact rails, and power distribution components benefit from materials that resist arcs caused by high currents and environmental factors.
- Renewable Energy Installations: Solar inverters, wind turbine converters, and battery storage systems rely on arc-resistant materials to handle frequent switching and environmental exposure.
Properly choosing arc-resistant materials across these applications reduces the risk of equipment failure, unplanned downtime, and hazards to personnel.
Best Practices for Material Selection
Selecting materials for electrical systems requires a careful balance of electrical performance, mechanical durability, and environmental resilience. Here’s a deeper look at the essential considerations for choosing materials with optimal arc resistance.
Assess Operating Conditions
Understanding the environment where the material will be used is critical. Factors such as voltage, current, temperature fluctuations, humidity, exposure to chemicals, and dust can significantly influence performance. Materials must withstand normal operating conditions, occasional surges, and transient faults.
Proper evaluation of these parameters helps ensure the material will resist electrical stress and mechanical wear over time. Additionally, considering extreme conditions or potential contamination prevents premature failures and maintains consistent system safety.
Review Arc Resistance Ratings
Arc resistance ratings provide a quantitative measure of a material’s ability to withstand electrical arcing. Engineers should reference standardized tests, such as ASTM D495 or IEC 60112, to compare materials objectively.
Selecting materials based on verified arc resistance ensures the system can handle short circuits, surges, and accidental arcing without degradation. It is also essential to interpret these ratings in the context of real-world operating conditions, considering temperature, humidity, and potential contamination.
This step ensures that the chosen material maintains performance under both normal and fault conditions, reducing downtime and enhancing safety.
Consider Mechanical and Thermal Properties
Materials must endure electrical stress, mechanical, and thermal challenges. Vibration, impact, and thermal cycling can degrade material integrity over time, reducing arc resistance and increasing failure risk.
Evaluating tensile strength, hardness, thermal conductivity, and expansion coefficients helps in selecting materials that maintain structural and electrical integrity. Properly matched mechanical and thermal properties prevent cracking, deformation, or insulation breakdown, ensuring reliable performance.
This approach enhances system safety, avoids unexpected downtime, and protects expensive equipment from unnecessary wear or damage.
Check Compliance and Standards
Ensuring that materials comply with industry standards is critical for safety and operational reliability. Standards such as ASTM, IEC, and UL provide guidelines for electrical, mechanical, and thermal performance, helping engineers choose materials that meet rigorous testing requirements. Compliance ensures that the material will behave predictably under fault conditions, protecting both personnel and equipment.
Additionally, using standardized materials simplifies audits, reduces liability, and allows manufacturers to maintain consistency across products. Adhering to these standards is an essential step in designing durable and safe electrical systems.
Factor in Maintenance and Longevity
Long-term reliability is closely tied to material durability and ease of maintenance. Materials with high arc resistance that also resist chemical degradation, moisture, and mechanical wear require fewer replacements or inspections.
Choosing materials with predictable aging behavior allows engineers to plan maintenance schedules efficiently, reducing unexpected downtime. Longevity considerations also include cost-effectiveness over the system’s life cycle, balancing upfront material cost with reduced maintenance and replacement needs.
Prioritizing durable, resilient materials safeguards operational continuity, protects equipment investments, and ensures personnel safety over the long term.
Ensure Optimal Arc Resistance with LSElectric America Inc.
Selecting materials with high arc resistance is critical for safety, reliability, and long-term performance in electrical systems. LSElectric America Inc. provides a comprehensive range of power distribution devices, switchgear, and protection solutions that meet the most demanding operational and environmental conditions.
- Switchgear – Comprehensive, reliable systems for medium and low voltage applications.
- VCB, ACB & MCCB – Circuit breakers and switch-disconnectors engineered for high performance and arc-resistance.
- Transformers – Cast resin and other designs optimized for safe, continuous operation.
Partner with LSElectric to protect equipment, reduce downtime, and ensure personnel safety through materials and solutions engineered for superior arc resistance. Explore the right products for your system.