Meta Description: Disconnect switches ensure safety and protect equipment by isolating power. Learn their types, functions, and key uses in electrical systems.
What Is a Disconnect Switch and Why Is It Essential for Safety?

Electrical accidents remain a serious concern in industrial and commercial settings. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, more than 5,000 workers suffer fatal electrical injuries annually in the U.S. alone, many of which occur during maintenance or equipment servicing without proper isolation protocols in place.
This is where disconnect switches play a vital role in protecting personnel and preventing costly damage.
In this blog, we’ll explore what disconnect switches are, how they work, the types available, and how to choose the right one for your electrical system.
What Is a Disconnect Switch?
| A disconnect switch is a manually operated device that isolates electrical equipment from its power source. Its primary role is to ensure safety by de-energising a circuit before maintenance, inspection, or emergencies. |
Disconnect switches are not meant to interrupt current under load but to provide a visible and reliable means of disconnection when the system is off.
They are commonly installed in industrial, commercial, and residential settings to prevent accidental energisation and protect personnel during servicing.
Typical features of a disconnect switch include:
- Manual operation – Allows complete control over when the circuit is isolated
- Visible break – Confirms that the circuit is entirely disconnected
- Enclosure options – Indoor or weatherproof versions based on the environment
- Fused or non-fused – Protection against overcurrent (fused) or simple disconnection (non-fused)
- Voltage and current ratings – Tailored to match the system requirements
These switches guard against overload, helping to prevent damage caused by excessive current.
Importance of a Disconnect Switch
What role does a disconnect switch play in your commercial, industrial, or residential electrical setup? Here’s why having one is essential:
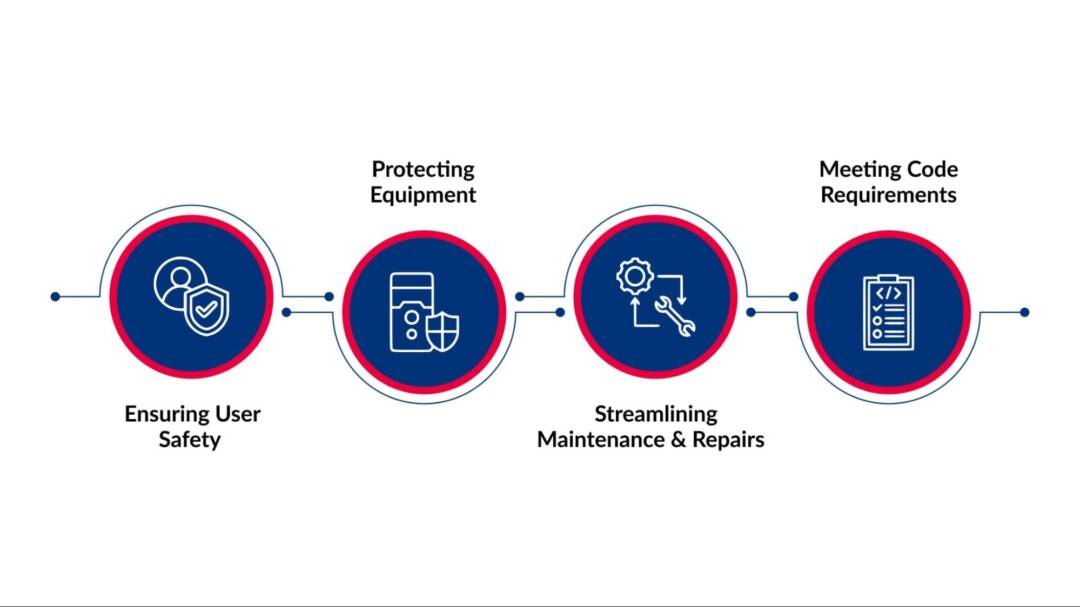
Ensuring User Safety
Safety is always the top priority. A disconnect switch provides a straightforward way to cut off power quickly in emergencies, reducing the risk of electrical shocks, burns, or worse.
By isolating power to an entire system or specific sections, it protects anyone working on or near electrical equipment from potential hazards.
Protecting Equipment
Beyond safeguarding people, disconnect switches help prevent damage to electrical devices. Overloads, short circuits, and faults can seriously harm equipment, often leading to costly repairs or replacements.
Having a visible and accessible disconnect point allows for swift power interruption, minimizing potential damage and saving time and money, especially important in environments with expensive machinery.
Streamlining Maintenance & Repairs
Maintenance teams rely on disconnect switches to safely service or upgrade electrical systems. Being able to isolate a particular circuit or device without shutting down an entire facility improves work efficiency and reduces downtime. This localized control is critical in commercial and industrial operations where continuous productivity is essential.
Meeting Code Requirements
Installing disconnect switches is often legally required. The National Electrical Code (NEC), for example, mandates accessible disconnects for motor-driven equipment and other specific installations. Compliance with these regulations ensures safety and helps avoid legal consequences such as fines or penalties.
Types of Disconnect Switches
Disconnect switches come in several configurations tailored to specific electrical systems, environments, and safety requirements. Choosing the right type depends on factors such as load type, voltage level, enclosure rating, and operational conditions. Below are the most common types used across industrial and commercial applications:
Fused Disconnect Switches
Fused disconnect switches combine manual isolation with short-circuit protection. Inside the enclosure, the switch is paired with fuses that blow during overcurrent events. This type is often preferred in systems where additional circuit protection is needed to safeguard equipment and personnel.
Fused models are commonly found in motor control centers, lighting panels, and industrial machinery setups. They also allow for easier coordination with other protection devices downstream. While these switches may require occasional fuse replacement, they offer reliable performance and are a standard choice for NEC-compliant installations in heavy-duty environments.
Non-Fused Disconnect Switches
Non-fused disconnect switches provide a straightforward means to isolate power without any built-in overcurrent protection. These are often used in systems where separate circuit breakers or fuses already handle fault protection. ]
Non-fused models are suitable for applications where the goal is strictly mechanical disconnection, such as servicing HVAC units or other non-motorized systems.
Their simple design makes them cost-effective and easy to operate, especially in areas where space is limited. These switches are commonly installed close to equipment, enabling maintenance crews to cut power quickly before beginning work.
Load Break Switches
Load break disconnect switches interrupt current under load safely. Unlike basic isolators, they feature arc-extinguishing mechanisms to handle switching while the circuit is energized. This makes them especially useful in medium-duty to high-duty applications, such as transformer isolation, motor control, or renewable energy systems.
These switches are built to withstand repeated operation and are often part of switchgear panels where frequent switching is required. Their reliability in live circuit conditions adds an extra layer of operational flexibility and safety.
Double Throw (Transfer) Switches
Double-throw disconnect switches allow power to be routed between two sources or two different loads. They are typically used in applications where redundancy is critical, such as backup generator systems or dual-supply commercial installations.
By flipping the switch, operators can move electrical load from the primary source to a secondary one without delay. This type of disconnect switch is essential for maintaining continuity during power outages or supply shifts. Many models are manually operated, but motorized versions are available for automated switching needs.
Types of Disconnect Switches by Mode of Operation
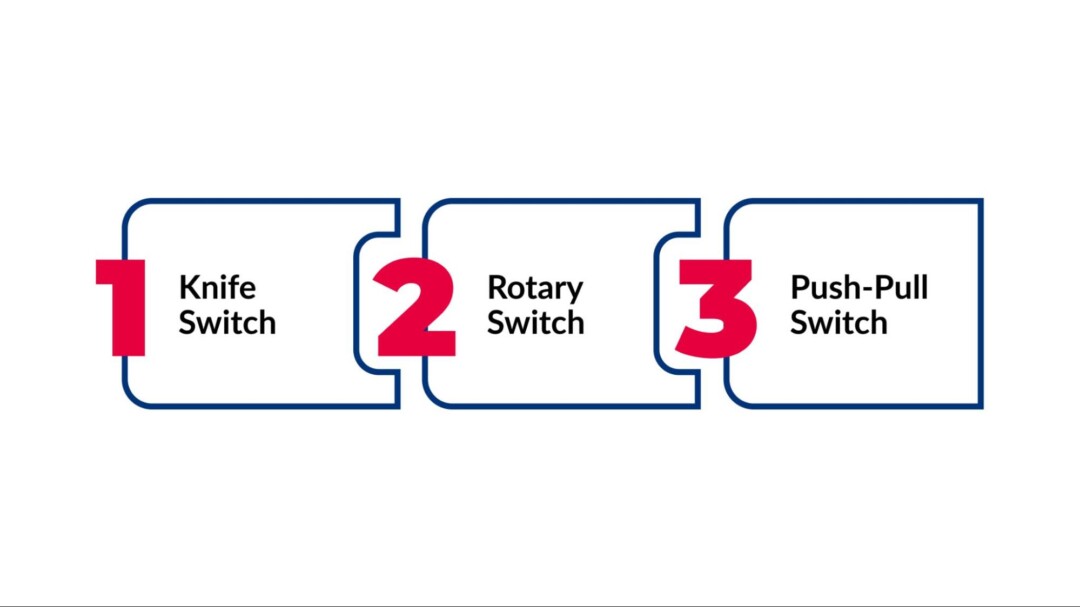
Disconnect switches are often classified by how they operate, with common types including rotary, knife, and push-pull switches.
Knife Switch
This is one of the simplest and most recognizable styles. It uses a flat metal blade that is manually lifted or lowered to make or break an electrical connection. Knife switches are frequently found in specialized industrial settings where a straightforward, visible disconnection method is preferred.
Rotary Switch
Operating through a turning mechanism, rotary switches enable the user to rotate a contact arm into or out of a fixed contact to control the flow of electricity. These switches are user-friendly and typically can be locked in the off position to enhance safety during maintenance or emergencies.
Push-Pull Switch
This type employs a push-and-pull motion to engage or disengage the electrical connection. Push-pull disconnect switches are designed for environments where frequent operation is expected, offering durability and ease of use in demanding applications.
Disconnect Switches vs. Circuit Breakers
While both disconnect switches and circuit breakers play important roles in electrical systems, they serve different purposes. A disconnect switch is primarily used to isolate a portion of the electrical circuit for maintenance or emergency shutdown, ensuring that a specific section is completely de-energized and safe to work on. However, disconnect switches do not protect against overloads or short circuits. They simply open or close the circuit manually or mechanically.
Circuit breakers, on the other hand, are protective devices that automatically interrupt electrical flow when they detect an overload or short circuit. They safeguard the electrical system by preventing damage and reducing fire risks, but they may not always guarantee a visibly open circuit for maintenance purposes.
In many systems, both devices are used together: disconnect switches provide a safe means to isolate equipment, while circuit breakers offer automatic protection.
| Feature | Disconnect Switch | Circuit Breaker |
| Primary Function | Manually isolates electrical circuits for safety and maintenance | Automatically interrupts electrical flow during faults |
| Overload Protection | No | Yes |
| Short Circuit Protection | No | Yes |
| Operation | Manual or mechanical | Automatic with manual override |
| Visible Break | Typically provides visible open contacts | Usually no visible break |
| Resetting | Must be manually closed | Can be reset manually or automatically |
| Typical Use Cases | Maintenance isolation, emergency shutdown | Overcurrent and fault protection |
| Safety Role | Ensures de-energized circuits for safe work | Prevents damage and hazards caused by faults |
| Installation Location | Near equipment or panels for easy access | Integrated within electrical panels |
Applications of Disconnect Switches
Disconnect switches’ ability to stop power flow instantly makes them critical in both routine operations and emergency scenarios.
Common applications include:
- Industrial machinery: Allows safe equipment maintenance without shutting down the entire production line.
- Power distribution panels: Offers localized control during upgrades, expansions, or fault isolation.
- HVAC systems: Provides shutoff access for technicians servicing air conditioning units, chillers, and ventilation equipment.
- Solar and renewable energy systems: Ensures safe disconnect for solar inverters or battery storage maintenance.
- Commercial buildings: Protects lighting systems, elevators, and pumps with dedicated disconnect points.
- Utility substations: Enables fast power isolation during grid faults or scheduled work.
- Agricultural and outdoor systems: Safeguards irrigation controls, grain dryers, and outbuilding circuits.
Installation and Maintenance of Disconnect Switches
A disconnect switch plays a vital role in electrical safety and system protection. Selecting and maintaining the right switch involves careful attention to several important factors.
- Proper Sizing: The switch must match the application’s requirements, including its electrical ratings such as voltage, current, and horsepower. It should also fit securely in the allotted space to avoid movement or mechanical stress. An incorrectly sized switch risks failure and safety hazards.
- Correct Mounting: Disconnect switches come with different mounting options like DIN rail, panel mount, wall or box mount, flange mount, and base mount. Choosing the right mounting style depends on the equipment and environment to ensure secure installation and easy access.
- Regular Inspection: Compliance with safety standards like UL 98, UL 508, NEC Article 430, and IEC is essential to ensure the switch has been properly tested and certified. Routine inspections and tests help detect any wear, damage, or operational issues early, keeping systems reliable and safe.
- Proper Labeling: Clear labels indicating the switch’s function, ratings, and the equipment it controls are crucial. Labels help prevent mistakes during operation. Additionally, disconnect switches should support lockout/tagout procedures to prevent accidental power restoration during maintenance.
- Enclosure Rating: The enclosure type must suit the location and environment. For instance, outdoor installations require enclosures rated to protect against weather, dust, and debris (like NEMA 3R), while indoor settings might only need simpler enclosures (such as NEMA 1). Choosing the right enclosure ensures durability and safety.
Proper installation and maintenance set the stage for long-term electrical safety and performance. To support those standards, LS Electric offers a trusted range of disconnect switches and MCCBs engineered for reliability in demanding environments.
Power Your System Safely with LS Electric America Inc.’s MCCBs & Switches
When it comes to reliable and high-performance disconnect switches and circuit breakers, LS Electric America Inc. is your trusted partner. Our comprehensive product lineup enhances safety, durability, and operational efficiency across various applications.
Explore LS Electric’s advanced solutions, including:
- DC Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCB) & Switch-Disconnectors
- DC Air Circuit Breakers (ACB) & Switch-Disconnectors
- DC Compact Switch-Disconnectors
- DC UL-Certified Switch-Disconnectors
Upgrade your electrical systems with LS Electric’s cutting-edge products to ensure maximum protection, compliance, and seamless power management. Reach out today to learn more about how LS Electric can empower your operations.