According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global electricity consumption is projected to grow at an average annual rate of nearly 4% from 2025 through 2027. This accelerating demand places greater pressure on electrical infrastructure to deliver uninterrupted, safe, and efficient power.
However, many systems remain vulnerable to faults, overloads, operational inefficiencies, risks resulting in equipment failure, safety incidents, and costly downtime. Switchgear plays a critical role in mitigating these risks.
| “Switchgear” describes the circuit breakers, fuses, and electrical disconnect switches that isolate, control, and safeguard electrical equipment. In simple terms, switchgear electrical systems manage the flow of electricity and protect circuits from damage due to faults like short circuits or overloads. Whether you’re in a power plant, data center, or large commercial building, switchgear ensures safe and reliable electrical power distribution. |
In this blog, we will discuss switchgear, how it works, its components and applications, and how LS Electric America’s solutions meet the performance, safety, and compliance standards required by today’s power systems.
Components of Electrical Switchgear
A switchgear assembly comprises several major components that work together to control, protect, and isolate electrical equipment:
-
Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers are crucial elements in switchgear systems. They automatically disconnect the electrical flow in case of a fault, such as a short circuit or overload. This prevents equipment damage and ensures safety throughout the system.
-
Disconnect Switches
Disconnect switches safely isolate equipment during maintenance or repairs. By physically severing the electrical connection, they eliminate the risk of accidental energization, ensuring worker safety.
-
Fuses
Fuses offer protection by melting and breaking the circuit when excessive current flows through them. They are a simple yet effective method for preventing damage to sensitive equipment.
-
Fault interrupters
Fault interrupters function similarly to circuit breakers but are often designed for specific fault conditions. These self-contained devices detect abnormal current levels and interrupt power without reclosing automatically. Their built-in control elements make them highly responsive and reliable for managing faults.
-
Relays
Relays act as intelligent sensors and controllers, continuously monitoring electrical parameters and triggering protective actions when necessary. They are essential for automation and quick response in modern systems.
-
Control Panel
Lastly, control panels serve as the operational center. They house switches, indicators, and monitoring tools that allow operators to manage, supervise, and respond to conditions across the switchgear system.
How Does a Switchgear Work?
Here’s a breakdown of how switchgear operates:
Normal Operation
During normal conditions, the switchgear allows current to pass from the power source to the load. It continuously monitors voltage, current, frequency, and power factors to ensure operational parameters are within predefined thresholds. This helps maintain optimal system performance and prevents unnecessary interruptions.
Fault Detection
Sensors and protective relays continuously monitor the circuit for any signs of abnormal conditions. When a fault occurs, such as a short circuit, overload, or ground fault, the relays detect the anomaly within milliseconds, ensuring rapid response times.
Circuit Interruption
Upon detecting a fault, the protective relay sends a signal to the circuit breaker, interrupting the current and isolating the faulty section. The breaker immediately disconnects the problematic area, preventing equipment damage and allowing the rest of the system to remain operational. Depending on the breaker type, the interruption occurs in different ways:
- Vacuum Circuit Breakers (VCB): Use a vacuum to extinguish the arc created when disconnecting the current. These are commonly used in medium-voltage systems.
- Air Circuit Breakers (ACB): Rely on air to extinguish the arc. They are typically used in low-voltage systems for overcurrent and short-circuit protection.
- SF6 Circuit Breakers: These use sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) gas as the dielectric medium to extinguish the arc. They are found in high-voltage systems and are known for their compact design and high reliability.
- Oil Circuit Breakers: Oil is commonly used in older systems as an insulating and arc-extinguishing medium.
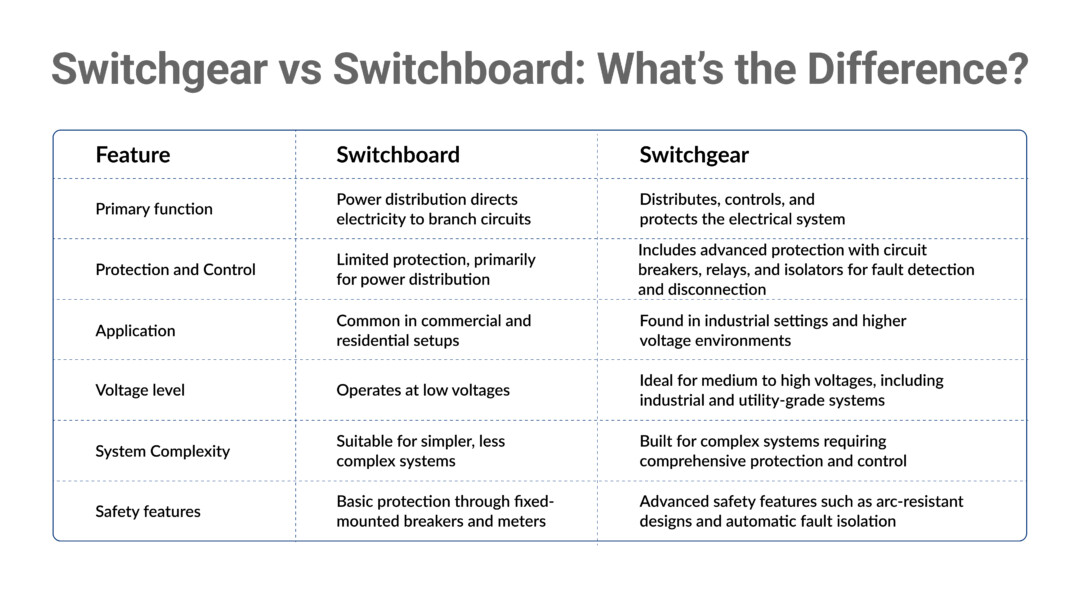
Switchgear vs Switchboard: What’s the Difference?
While switchgear and switchboards are vital components in electrical systems, they serve different roles and are utilized for distinct applications.
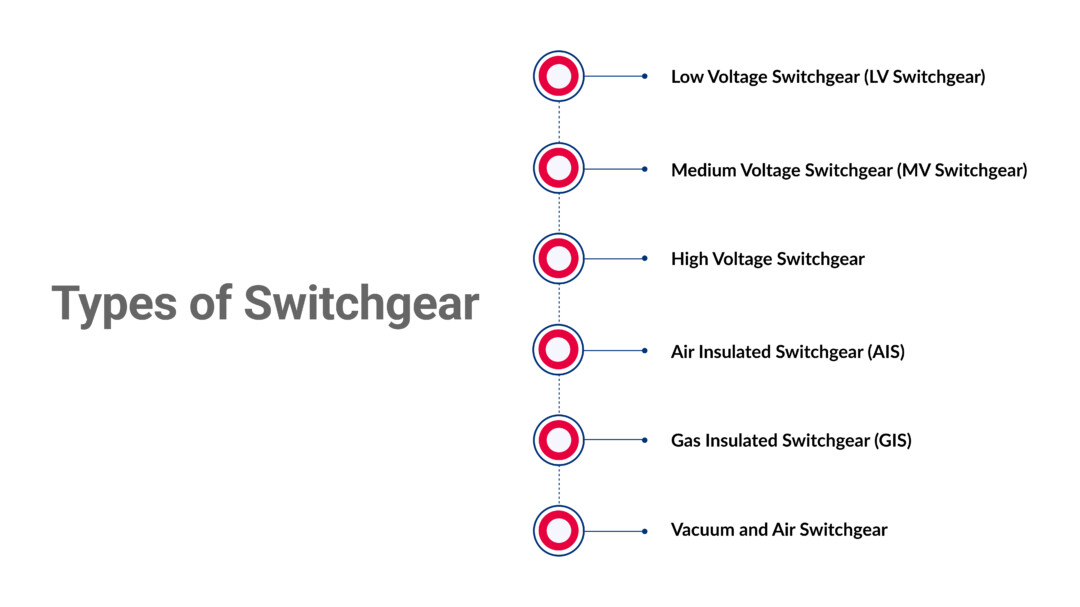
Types of Switchgear
Switchgear comes in various types, each managing different voltage levels and application needs. It ensures safety, control, and efficient power distribution from low to high voltage systems. Understanding the types of switchgear is essential for selecting the right solution for industrial, commercial, or utility-grade electrical systems.
Low Voltage Switchgear (LV Switchgear)
Low-voltage switchgear operates at voltages up to 1,000 volts. It is commonly used in residential and commercial buildings. LV switchgear includes components like:
- Circuit breakers
- Disconnectors
- Contactors
LS Electric offers UL Low-Voltage Switchgear and UL891 Switchboard Solutions, which are known for high performance, durability, and safety. They are engineered for optimal safety and performance in demanding environments. Built with an arc-resistant structure, they ensure personnel protection and property safety.
With high short circuit withstand ratings and modular, space-saving designs, it supports up to 6,000A and guarantees long-term reliability in critical applications.
Medium Voltage Switchgear (MV Switchgear)
Medium-voltage switchgear handles voltages between 1kV and 36kV. It is commonly found in industrial facilities, utility substations, and infrastructure projects.
LS Electric manufactures reliable metal-clad switchgear, such as the MCSG (Metal Clad Switchgear), which provides safe and efficient power distribution. LS Electric’s MCSG (Metal Clad Switchgear) offers complete protection and high performance with vacuum circuit breakers rated up to 38kV and 40kA.
Certified under UL and IEEE standards, it ensures arc resistance, modular accessibility, and space efficiency—ideal for power plants, semiconductor industries, and transportation hubs where safety and reliability are critical.
High Voltage Switchgear
High-voltage switchgear operates above 36kV and is commonly used in power generation plants and transmission substations. It is designed to handle the high electrical stresses of large-scale energy systems, ensuring safe and reliable power distribution over long distances.
These systems feature advanced insulation and arc protection to isolate faults and protect equipment quickly. High-voltage switchgear is important for grid stability, preventing large-scale outages and ensuring continuous operation.
Air Insulated Switchgear (AIS)
Air-insulated switchgear (AIS) uses air for insulation and is cost-effective and easy to maintain. It is often used in power distribution systems and industrial plants where space is not an issue.
However, AIS requires more physical space than other types, which can be a limitation in congested environments. Despite this, its reliability and lower upfront cost make it a common choice for many applications.
Gas Insulated Switchgear (GIS)
Gas-insulated switchgear (GIS) uses SF6 gas for insulation, providing a compact, reliable solution for high-voltage systems. Due to its smaller size, GIS is ideal for space-limited environments like urban substations and underground facilities.
It offers superior reliability and safety, as the sealed system is protected from external factors like dust and moisture. GIS requires less maintenance and is highly effective in preventing electrical faults.
Vacuum and Air Switchgear
Vacuum switchgear uses a vacuum to extinguish the arc during circuit interruptions, making it highly effective for medium-voltage systems. It requires less maintenance and offers fast switching capabilities.
On the other hand, air switchgear uses air for arc extinction and is commonly found in low-voltage applications. While bulkier and needing more space, air switchgear remains a reliable, cost-effective option for residential and smaller commercial setups.
Things to Consider When Selecting Switchgear for Your Industry
Choosing the right switchgear is critical to ensure your electrical systems’ safe, reliable, and efficient operation. Here are the major factors to consider when selecting switchgear for your industry:
Voltage Level: Switchgear needs to match your system’s voltage requirements. Low-voltage switchgear (up to 1kV) is suitable for low-voltage applications, while medium (1kV-36kV) and high-voltage (above 36kV) switchgear are required for industrial plants, substations, and power generation facilities.
Environmental Conditions: Consider whether the switchgear will be installed indoors or outdoors. Outdoor switchgear should withstand ecological conditions like extreme weather, moisture, and dust. For indoor use, consider factors like space constraints and ease of maintenance.
Safety and Protection Features: Your switchgear should have built-in protection against faults such as short circuits or overloads. Look for systems with advanced safety features, such as arc-resistant designs, which help prevent equipment damage and protect personnel.
Space and Modularity: Space limitations in your facility can influence the type of switchgear you choose. Compact options, like gas-insulated switchgear (GIS), are ideal for environments with space constraints. Additionally, modular switchgear allows for future expansion and flexibility in adapting to evolving needs.
Compliance with Industry Standards: Ensure that the switchgear complies with relevant industry standards such as UL (Underwriters Laboratories), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), or IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers). These certifications ensure the equipment meets safety, performance, and reliability requirements.
Maintenance Requirement: Different types of switchgear have varying maintenance needs. Some may require regular servicing and inspections, while others, like gas-insulated switchgear (GIS), are virtually maintenance-free for extended periods. Consider the availability of spare parts and ease of servicing when making your decision.
Cost vs. Long-Term Reliability: While initial costs are a factor, don’t overlook the switchgear’s long-term reliability and efficiency. Opt for high-performance and durable equipment, minimizing future operational downtime and maintenance costs.
Applications of Switchgear Power Systems
Switchgear power systems are used across a wide range of applications:
Utilities
Switchgear plays a vital role in utility substations by controlling, protecting, and isolating electrical equipment. It ensures safe grid operations, supports fault detection, and allows maintenance without interrupting power supply across large distribution networks.
Industries
Industrial facilities rely on switchgear for continuous, high-capacity power distribution and protection against electrical faults. In critical operations such as mining or petrochemical processing, switchgear enhances safety, minimizes downtime, and manages load fluctuations to maintain efficient production.
Commercial buildings
Commercial buildings use switchgear systems to manage large-scale electrical loads safely and reliably. Hospitals and airports, in particular, benefit from switchgear’s fault isolation and backup integration, ensuring vital systems remain operational during outages or electrical disturbances.
Data Centers
Data centers depend on switchgear for uninterruptible power delivery and efficient fault management. It enables seamless switching between primary and backup systems, protects servers from surges, and supports power monitoring to maintain uptime and data integrity.
Renewable energy
Switchgear in renewable energy systems ensures the safe integration of variable power sources into the grid. It manages load balancing, protects sensitive equipment, and isolates faults in solar or wind farms to optimize energy output and reliability.
Discover the Right Switchgear for Your Power System with LSElectric America Inc.
A quality switchgear must be:
- Safe and reliable
- Compliant with international standards
- Durable under varying environmental conditions
- Easy to maintain and install
LS Electric America meets all these standards with its range of switchgear electrical products. Whether you’re looking for pad-mounted switchgear for outdoor use or compact indoor systems, we offer innovative, certified solutions. Our advanced switchgear solutions ensure reliability, safety, and efficiency for diverse power applications.
Check out our range of switchgear products and discover how LS Electric America can help meet your energy management needs today.